Ion exchange resin is a kind of insoluble macromolecule spherical granular polymer, which is synthesized from styrene, acrylic acid and propylene ester. It is a three-dimensional spatial reticular structure gene generated by polymerization reaction and then introduced into different types of chemical active groups.
Ion exchange resins are divided into two categories: cationic resins and anionic resins. Cationic resins are divided into strong acidic resins and weak acidic resins. Anionic resins are divided into strong alkaline resins and weak alkaline resins.
Structures of ion exchange resins:
Ion exchange resins consist of three parts: insoluble three-dimensional reticulated polymer skeleton, ionic functional groups connected to the skeleton and exchangeable ion pore with opposite charges on the functional groups.
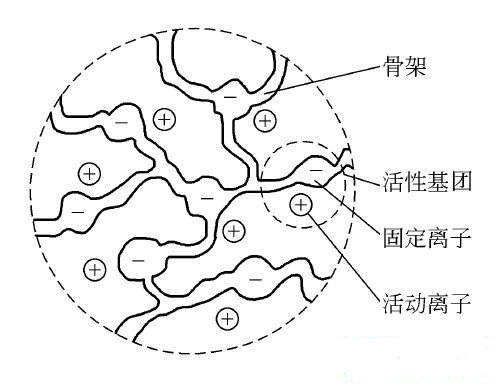
Polymer skeleton: It is composed of crosslinked polymer, such as crosslinked polyphenylene, polyacrylic acid, etc.
Ion Exchange Groups: It is attached to the polymer skeleton, with exchangeable ions (called counter ions) such as - SO3Na, - COOH, - N (CH3) 3Cl, or polar non-ionic functional groups such as - N (CH3) 2, - N (CH3) H, etc.
Hole: it is the pore between the pore structure (the gel pore) and the polymer structure in the dry and wet ion exchange resin (Mao Xikong).
On the cross-linked polymer matrix (skeleton), many exchange groups are bonded by chemical bonds. These exchange groups are also composed of two parts: the fixed part and the active part. The fixed part of the exchange group is bound to the polymer matrix and can not move freely, so it is called fixed ion. The active part of the exchange group is the ion opposite to the symbol of the binding of the fixed ion by ion bond, which is called counter ion or exchangeable ion. Antiions can dissociate into free-moving ions in solution. Under certain conditions, they can exchange with other counterions with the same symbols.
