成都森格尔环保科技有限公司
Chengdu senge environmental protection technology co.LTD
Consultation Hotline:02865357899
Production, Sales and Development of Ion Exchange Resin
成都森格尔环保科技有限公司
Chengdu senge environmental protection technology co.LTD
Consultation Hotline:02865357899
Production, Sales and Development of Ion Exchange Resin
Contact person: Manager Liu
Location: 028-65357899
Mobile phone: 15680686111
Mailbox: chengdu@sgrhb.com
Fax: 028-65357899
Email: chinaresin@sgrhb.com
Website: www.sgrhb.com
Website : en.sgrhb.com
Address: 79 Jiujin Street, Wuhou District, Chengdu City, Sichuan Province
It contains a large number of strong acidic groups, such as sulfonic acid-SO3H, which is easy to dissociate H+, so it has strong acidity. After resin dissociation, the negative ions (such as SO3-) contained in the body can adsorb other cations in the solution. These two reactions result in the exchange of H + in the resin with cations in the solution. Strong acidic resin has strong dissociation ability and can exchange ion in acidic or alkaline solution.
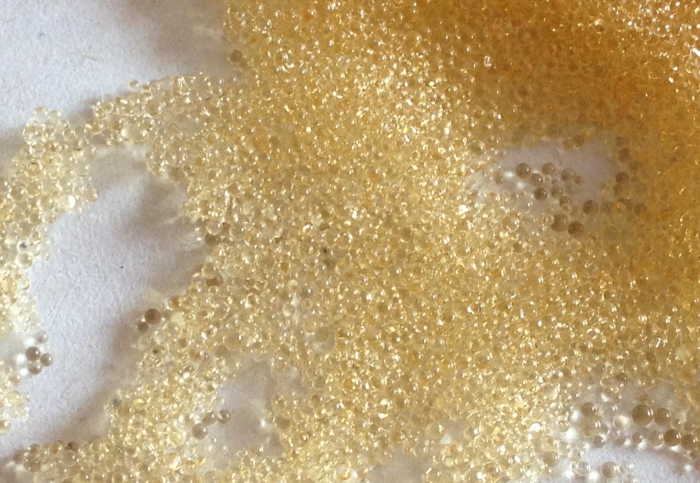

After the resin is used for a period of time, the resin should be regenerated, that is, the ion exchange reaction takes place in the opposite direction with the chemical agent, so that the functional groups of the resin can be restored to their original state for reuse. Ion exchange resin is composed of classification name, skeleton (or gene) name and basic name. The pore structure is divided into two types: gel type and large pore type. All macroporous resins with physical pore structure are added "big hole" before the full name. If the classification is acidic, the word "yang" should be added before the name, while the classification is alkaline, and the word "yin" should be added before the name. Such as: macroporous strong acidic styrene cation exchange resin. If the cationic resin is regenerated with strong acid, the resin releases the adsorbed cations and then binds with H + to restore the original composition.
2 and weakly acidic cationic resins
Containing weak acidic groups, such as carboxyl-COOH, they can separate H+ from water into acidity. Residual anions after resin dissociation, such as R-COO-(R is a hydrocarbon group), can be adsorbed with other cations in solution to form cation exchange. The resin has weak acidity and is difficult to dissociate and exchange ions at low pH. It can only be used in alkaline, neutral or slightly acidic solutions (e.g. PH5-14). These resins are also regenerated with acid (which is easier to regenerate than strong acidic resins).
3 and Strong Basic Anionic Resin
Containing strong alkaline groups, such as quaternary amines (also known as quaternary amines) - NR3OH (R is alkyl), they can dissociate OH - from water, showing a strong basicity. Ion exchange resin is composed of classification name, skeleton (or gene) name and basic name. The pore structure is divided into two types: gel type and large pore type. All macroporous resins with physical pore structure are added "big hole" before the full name. If the classification is acidic, the word "yang" should be added before the name, while the classification is alkaline, and the word "yin" should be added before the name. Such as: macroporous strong acidic styrene cation exchange resin. Ion exchange resins can be divided into styrene resin and acrylic resin according to their matrix types. The main properties and types of resins are determined by the types of chemical active groups in resins. Firstly, it can be divided into cationic resins and anionic resins, which can exchange ions with cations and anions in solution respectively. Cationic resins can be divided into strong acidity and weak acidity. Anionic resins can be divided into strong alkalinity and weak alkalinity. The resin has high dissociation and good performance under different pH conditions. It is regenerated from strong alkali such as NaOH.
4. Weak Basic Anionic Resin
Containing weak basic groups, such as primary amino group (also known as primary amino group) - NH2, secondary amino group (secondary amino group) - NHR, tertiary amino group (tertiary amino group) - NR2, they can dissociate OH-, showing weak alkalinity in water. In most cases, the resin adsorbs the entire acidic molecule in the solution. It can only work in neutral or acidic conditions, such as PH1-9. Na2CO3 and NH4OH are renewable.
Note: Strong alkaline and weak alkaline resins have positive charge groups, which bind to anions in solution, resulting in anion exchange. Ions (such as SO3-) can adsorb other cations in solution. These two reactions result in the exchange of H + in the resin with cations in the solution. Strong acidic resin has strong dissociation ability and can exchange ion in acidic or alkaline solution.
Chengdu Senger Environmental Technology Co., Ltd.
Record No: 蜀ICP备19000327号
Powered by Xiangyun Platform
Contact person: Manager Liu
Location: 028-65357899
Mobile phone: 15680686111
Email: chinaresin@sgrhb.com